Breadth First Search (BFS)
Overview
Visits nodes level by level in a graph or tree, starting from the closest nodes to the start point.
| Time | Space |
|---|---|
O(n) | O(n) |
Tree BFS
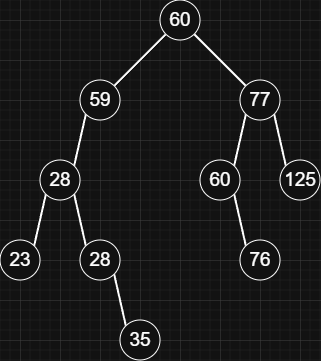
Example Tree:
Implementation:
Go to Binary Search Tree for the complete BST implementation.
This implementation uses a Queue data structure, so you must implement it beforehand.
class BinarySearchTree {
...
BFS() {
if (this.root === null) return null;
const list = [];
const queue = new Queue();
queue.enqueue(this.root);
while (queue.size > 0) {
const currNode = queue.peek();
list.push(currNode.value);
if (currNode.left) {
queue.enqueue(currNode.left);
}
if (currNode.right) {
queue.enqueue(currNode.right);
}
queue.dequeue();
}
return list;
}
}Usage:
const tree = new BinarySearchTree(); ... console.log(tree.BFS()); // [60, 59, 77, 28, 60, 125, 23, 28, 76, 35]
Graph BFS
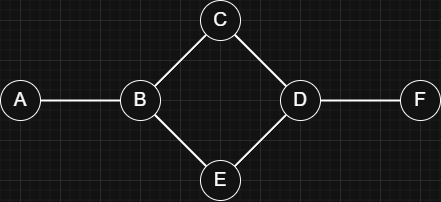
Example Graph:
Adjacency Matrix
Implementation:
This implementation uses a Queue data structure, so you must implement it beforehand.
const adjacencyMatrix = {
A: { A: 0, B: 1, C: 0, D: 0, E: 0, F: 0 },
B: { A: 1, B: 0, C: 1, D: 0, E: 1, F: 0 },
C: { A: 0, B: 1, C: 0, D: 1, E: 0, F: 0 },
D: { A: 0, B: 0, C: 1, D: 0, E: 1, F: 1 },
E: { A: 0, B: 1, C: 0, D: 1, E: 0, F: 0 },
F: { A: 0, B: 0, C: 0, D: 1, E: 0, F: 0 },
};
function adjMatrixBFS(start, graph) {
const seen = {};
const queue = new Queue();
queue.enqueue(start);
const values = [];
while (queue.size > 0) {
const node = queue.dequeue();
if (seen[node]) continue;
values.push(node);
seen[node] = true;
const connections = graph[node];
for (const key in connections) {
if (connections[key] > 0 && !seen[key]) {
queue.enqueue(key);
}
}
}
return values;
}Usage:
console.log(adjMatrixBFS('C', adjacencyMatrix)); // ['C', 'B', 'D', 'A', 'E', 'F'] console.log(adjMatrixBFS('A', adjacencyMatrix)); // ['A', 'B', 'C', 'E', 'D', 'F'] console.log(adjMatrixBFS('B', adjacencyMatrix)); // ['B', 'A', 'C', 'E', 'D', 'F']
Adjacency List
Implementation:
This implementation uses a Queue data structure, so you must implement it beforehand.
const adjList = {
A: ['B'],
B: ['A', 'C', 'E'],
C: ['B', 'D'],
D: ['C', 'E', 'F'],
E: ['B', 'D'],
F: ['D'],
};
function adjListBFS(start, graph) {
const seen = {};
const queue = new Queue();
queue.enqueue(start);
const values = [];
while (queue.size > 0) {
const node = queue.dequeue();
if (seen[node]) continue;
values.push(node);
seen[node] = true;
const connections = graph[node];
for (const key of connections) {
if (!seen[key]) {
queue.enqueue(key);
}
}
}
return values;
}Usage:
console.log(adjListBFS('C', adjList)); // ['C', 'B', 'D', 'A', 'E', 'F'] console.log(adjListBFS('A', adjList)); // ['A', 'B', 'C', 'E', 'D', 'F'] console.log(adjListBFS('B', adjList)); // ['B', 'A', 'C', 'E', 'D', 'F']
Matrix (2D Array) BFS
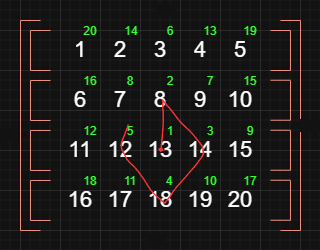
Example 2D Array:
The red line shows the search flow starting from points
row: 2andcol: 2(green numbers show the same in a simpler format).
Implementation:
This implementation uses a Queue data structure, so you must implement it beforehand.
const arr2d = [
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
[6, 7, 8, 9, 10],
[11, 12, 13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18, 19, 20],
];
const directions = [
[-1, 0], // up
[0, 1], // right
[1, 0], // down
[0, -1], // left
];
function matrixBFS(matrix, row, col) {
const seen = new Set();
const queue = new Queue();
queue.enqueue([row, col]);
const values = [];
while (queue.size > 0) {
const [row, col] = queue.dequeue();
if (row < 0 || row >= matrix.length || col < 0 || col >= matrix[0].length || seen.has(`${row}${col}`)) {
continue;
}
seen.add(`${row}${col}`);
values.push(matrix[row][col]);
for (let i = 0; i < directions.length; i++) {
const currDir = directions[i];
queue.enqueue([row + currDir[0], col + currDir[1]]);
}
}
return values;
}Usage:
console.log(matrixBFS(arr2d, 2, 2)); // [13, 8, 14, 18, 12, 3, 9, 7, 15, 19, 17, 11, 4, 2, 10, 6, 20, 16, 5, 1] console.log(matrixBFS(arr2d, 0, 0)); // [1, 2, 6, 3, 7, 11, 4, 8, 12, 16, 5, 9, 13, 17, 10, 14, 18, 15, 19, 20] console.log(matrixBFS(arr2d, 1, 0)); // [6, 1, 7, 11, 2, 8, 12, 16, 3, 9, 13, 17, 4, 10, 14, 18, 5, 15, 19, 20] console.log(matrixBFS(arr2d, 2, 3)); // [14, 9, 15, 19, 13, 4, 10, 8, 20, 18, 12, 5, 3, 7, 17, 11, 2, 6, 16, 1]